Why Price-to-Sales Ratios Matter to Investors
The Price-to-Sales (P/S) ratio gives investors a simple, straightforward tool to gauge the value of a company relative to its revenue. This ratio is particularly useful when analyzing companies that are not currently profitable but are generating significant revenues. It provides a different perspective than traditional valuation metrics, such as the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio, that are primarily based on net income.
Key Business or Financial Drivers
The P/S ratio is influenced by several key business or financial drivers. These include the company’s sales growth rate, operating margins, and the stability of its revenue streams. For example, a company with high sales growth and strong operating margins is likely to have a higher P/S ratio than a company with slower sales growth and weaker margins.
Sales Growth Rate
Investors should pay attention to the company’s sales growth rate as it directly affects the P/S ratio. A high sales growth rate can justify a high P/S ratio, as it indicates potential future profitability.
Operating Margins
The company’s operating margin is another critical factor. A company with strong operating margins demonstrates efficient operations and cost management, which could lead to increased profitability and a higher P/S ratio.
Expectations vs Reality
Investors often use the P/S ratio to form expectations about a company’s future performance. However, these expectations may not always align with reality. For example, a company with a low P/S ratio may seem undervalued, but if it has low sales growth or declining margins, its stock may not be a good investment. Conversely, a company with a high P/S ratio may appear overvalued, but if it has strong sales growth and improving margins, its stock could still be a good investment.
What Could Go Wrong
While the P/S ratio is a useful tool, it’s not without its risks. One of the major risks is that it doesn’t take into account a company’s profitability. As a result, a company with high sales but low or negative profits could have a misleadingly high P/S ratio. Therefore, it’s essential for investors to consider other financial metrics alongside the P/S ratio to get a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health.
Long-Term Perspective
From a long-term perspective, the P/S ratio can help investors identify potential investment opportunities. However, it should not be the sole basis for investment decisions. It’s important to consider other factors such as the company’s competitive position, industry trends, and macroeconomic conditions. These factors can have a significant impact on a company’s long-term sales growth and profitability, which in turn, can affect its P/S ratio.
Investor Tips
- Look beyond the P/S ratio: Consider other financial metrics and qualitative factors to get a comprehensive view of a company’s investment potential.
- Consider the industry context: Compare the company’s P/S ratio with its peers to get a sense of its relative value.
- Monitor changes over time: Keep an eye on changes in the company’s P/S ratio over time as it can signal shifts in the company’s financial performance.
This article is intended to provide a broad overview of the Price-to-Sales ratio and its role in equity analysis. It does not constitute investment advice and investors should conduct their own research or seek professional advice before making investment decisions.

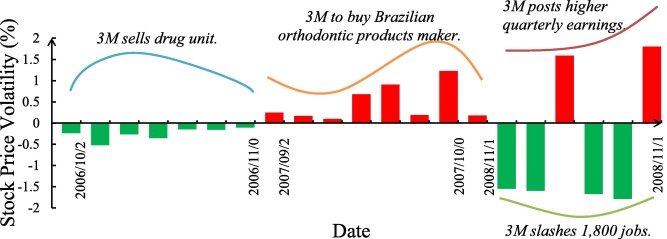

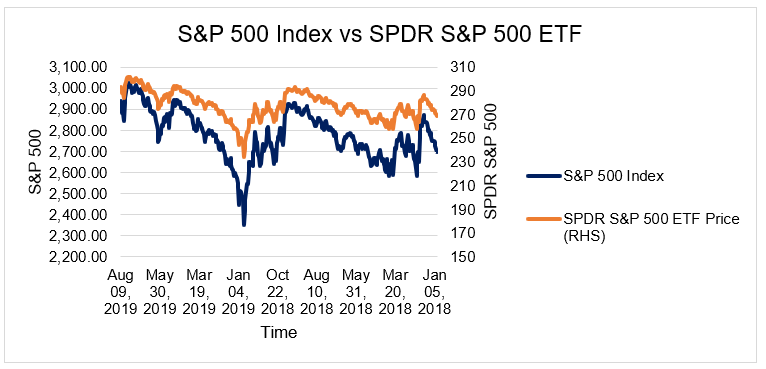
Leave a Reply