Introduction
Valuation models are fundamental tools used by investors to determine the intrinsic value of a stock and assess its potential for investment. Understanding the key takeaways from these models is crucial in making informed investment decisions and managing risks.
Key Business and Financial Drivers
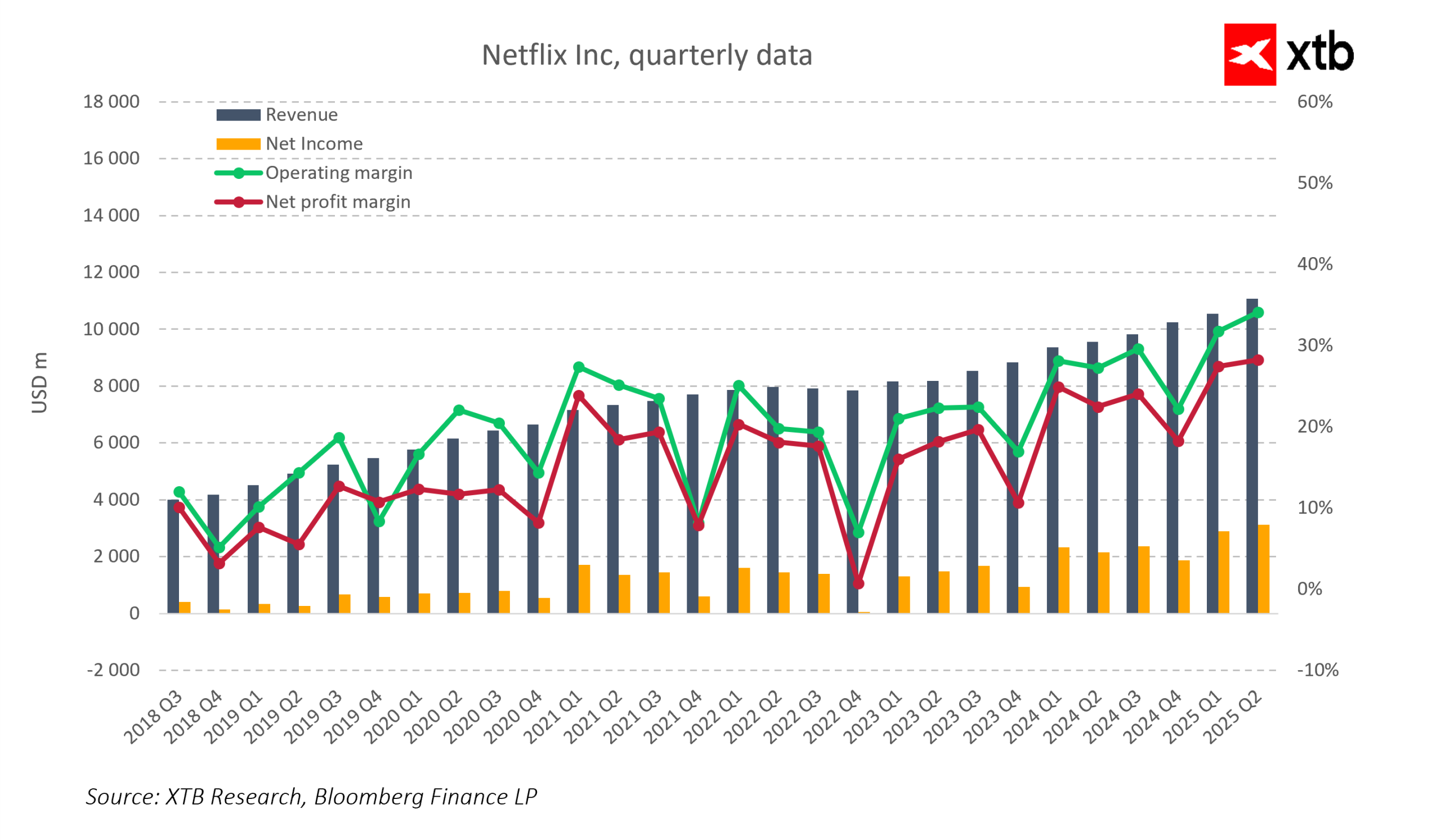
Valuation models are typically based on a company’s financial metrics, such as earnings, cash flow, and return on investment. These metrics are driven by the company’s operational efficiency, market positioning, and growth potential. Therefore, a thorough analysis of these drivers can provide insights into the company’s financial health and long-term profitability.
Operational Efficiency
One of the key business drivers is the company’s operational efficiency, which can be evaluated through metrics like operating margin and asset turnover. High operational efficiency often indicates a well-managed company that can deliver consistent returns over the long term.
Market Positioning
Market positioning refers to a company’s competitive standing in its industry. Companies with strong market positions often have more pricing power, which can lead to higher profit margins and stronger cash flows.
Growth Potential
Growth potential is another key business driver. Companies with high growth potential often command higher valuations because investors are willing to pay a premium for future earnings growth.
Expectations vs Reality
Valuation models are based on assumptions about future earnings and cash flows. However, these assumptions may not always align with reality. If a company’s actual performance falls short of the expectations built into its valuation, its stock price may decline. Therefore, it is crucial for investors to regularly revisit their assumptions and adjust their valuation models accordingly.
What Could Go Wrong
Several factors can negatively impact a company’s valuation. These include operational risks, market risks, and financial risks. Operational risks, such as supply chain disruptions or management turnover, can undermine a company’s efficiency and profitability. Market risks, such as changes in consumer preferences or competitive dynamics, can erode a company’s market position. Financial risks, such as higher interest rates or stricter regulations, can increase a company’s cost of capital and reduce its net income.
Long-Term Perspective
While short-term factors can cause temporary fluctuations in a company’s stock price, it’s the company’s ability to generate sustainable earnings and cash flows over the long term that ultimately drives its valuation. Therefore, investors should focus on the company’s long-term business fundamentals rather than getting swayed by short-term market noise.
Investor Tips
- Regularly review your valuation assumptions and adjust them based on the company’s latest financial results and market developments.
- Monitor the company’s operational efficiency, market positioning, and growth potential as these are key drivers of its valuation.
- Be aware of the potential risks that could negatively impact the company’s valuation and have a contingency plan in place.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Always do your own research and consult with a professional financial advisor before making any investment decisions.



Leave a Reply