Why “Normalization” Matters to Investors
When management mentions “normalization”, it often refers to the progression of business operations or financial metrics towards their long-term average or trend. It is a signal that the company believes temporary factors affecting its performance are subsiding. Understanding this concept is crucial for investors as it may indicate forthcoming changes in the company’s performance and thus, the stock’s value.
Key Business and Financial Drivers
Several drivers can lead to a period of normalization, including economic cycles, regulatory changes, product life cycles, and market competition. For instance, a company may see profits normalize after a period of regulatory scrutiny or after launching a successful product. The key is to identify these drivers and understand how they impact the company’s profitability and growth prospects.
Expectations Vs Reality
Investors tend to price in normalization based on management’s communication and their own assumptions about the future. However, the actual path to normalization can be different from expectations due to unforeseen challenges or opportunities. Therefore, it’s essential to monitor company updates and sector trends closely to adjust expectations accordingly.
What Could Go Wrong
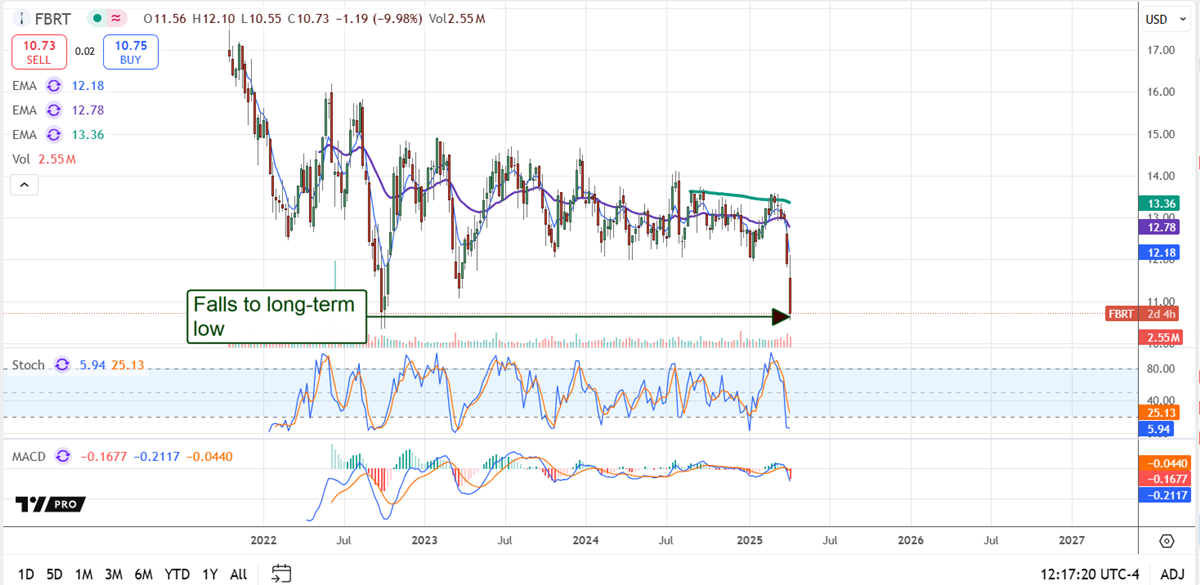
Normalization may not always lead to positive outcomes for investors. If the management’s assumptions about the business environment or the company’s operational efficiency prove incorrect, the expected normalization may not materialize. In some cases, normalization could mean returning to lower growth rates after a period of exceptional performance, which could negatively impact stock prices.
Long-Term Perspective
While normalization can cause short-term volatility, it is a part of the company’s long-term trajectory. Companies that successfully navigate normalization periods often emerge stronger, with more sustainable growth rates. Therefore, investors should view periods of normalization as potential opportunities to invest in companies at more reasonable valuations.
Investor Tips
- Listen carefully to management’s discussion of normalization during earnings calls and presentations.
- Monitor key business drivers that can impact the path to normalization.
- Be prepared for potential short-term volatility during periods of normalization.
- Consider the long-term implications of normalization on the company’s growth prospects.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always conduct your own research before making investment decisions.



Leave a Reply